What is Data Backup
It is critical to acknowledge that devices or servers may crash or be bypassed by a cybersecurity breach. The purpose of data backup and recovery is to ensure protection against loss of files, folders, or databases and establish a directory of restoration. Hardware/software issues and accidental deletion can be responsible for lost data. Having a robust security system will safeguard data and minimize the need to process a backup or recovery method.
Types of Data Backup
It is highly recommended for businesses to regularly perform data backups to avoid system failure, corruption, and imminent threats. There are three main backup types that are used. These include:
- Full backup – The process of creating a copy of all data files and saving them in a secure location to protect them
- Incremental backup – The process of backing all files that have been modified since the previous backup
- Differential backup – The process of backing all files that were modified since the previous full backup
On-Site vs. Cloud Back-up
There are two approaches used to back data up. The traditional way of storing files is through an on-site data backup procedure. For small businesses, these operations would be achieved through backing the data on a server or using a physical storage system such as an external hard drive or backup tape.
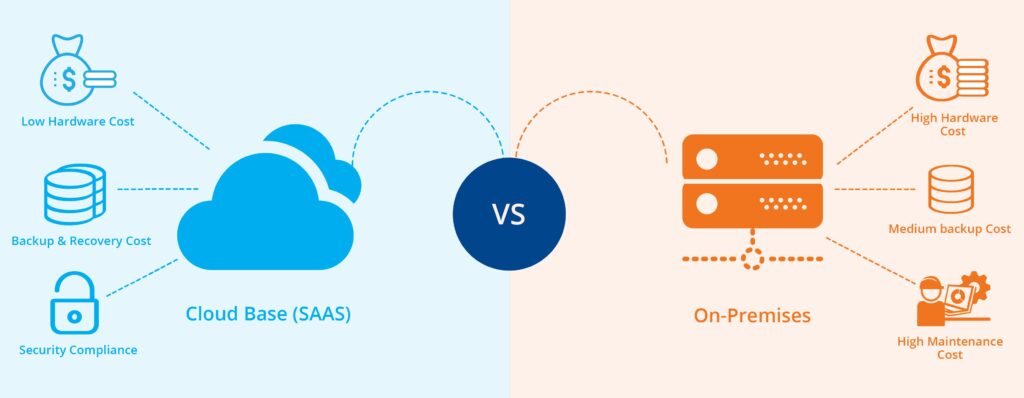
On-Site
Pros
- Allows the business to have full control over how data is stored and managed.
- Most time-effective measure to redress missing data.
- Insurance that no third-party software is involved and has access to your data.
- It may act as a more cost-effective measure compared to cloud-based backup services, which typically charge a subscription fee.
Cons
- Hardware issues may occur denying access to recovery options.
- The business is responsible for maintaining servers or hardware and is subject and liable to any technical failures.
- Although you pay for a one-time investment, on-site backup methods could require additional funding to upgrade, repair, or replace drivers, and maintain the network. If a business partners with an IT service company to provide network access, there may be an additional cost for security updates.
- Hardware is physical and thus may be stolen or damaged, resulting in lost data.
Cloud-Based Backups
Pros
- Extremely reliable service, as files are backed up every few minutes, and multiple copies are stored across many servers.
- Notable for its ease of access capabilities, almost anywhere and at anytime
- Although it seems unsafe, cloud-based backups are highly secure, as data is encrypted before being transferred.
Cons
- An internet connection is always required to be able to perform backups. A problematic situation may occur if a backup is needed to be performed during a power outage.
- Cloud backups are typically slower and may take longer to retrieve as data is transferred over the internet instead of a server or physical disk.
- Understand that the business is involved with a third party and is subject to their rules and protocols.
Considering Implementation
Businesses need to consider factors such as volume, budget, and backup recovery time objectives when selecting whether to implement an on-site or cloud-based recovery option. The next step is to examine how frequently backups should be instituted, especially if done manually. The timing of this backup would need to be assessed so that it does not interfere with business operations. Well-known backup software such as these will help protect and recover your files.
- Acronis True Image
- Veeam Backup & Replication
- EaseUS Todo Backup
Hardware options would include external hard drives or network-attached storage (NAS) solutions for businesses handling big data. When selecting a cloud-based service it is crucial to consider storage, security features, accessibility, and reliable technical support. Examples include
- Google Drive
- Backblaze
- Dropbox
Once installed, backups would need to be regularly tested to detect potential issues. For further security, consider encrypting your data to help protect it during transit.
References
Backup and Recovery. (n.d.). Cohesity. https://www.cohesity.com/glossary/backup-and-recovery/#:~:text=Backup%20and%20recovery%20is%20the
Marget, A. (2021, October 19). Types of Backup: Full, Incremental and Differential Backup. Unitrends. https://www.unitrends.com/blog/types-of-backup-full-incremental-differential#:~:text=Full%20backup%3A%20The%20most%20basic
Pros & Cons of Cloud-Based Backups vs. On-Site Backups. (2021, May 14). Ezcomputersolutions.com; EZComputer Solutions. https://www.ezcomputersolutions.com/blog/cloud-based-backups-vs-on-site-backups/
USGS. (n.d.). Backup & Secure | U.S. Geological Survey. Www.usgs.gov. https://www.usgs.gov/data-management/backup-secure
VpsCity. (n.d.). New Zealand’s Trusted Dedicated, Cloud, VPS & Hosting Provider. VpsCity. Retrieved August 2, 2024, from https://www.vpscity.co.nz/blog/101/On-Premise-vs-Cloud-Solutions-for-Enterprises.html